Your cart is empty
Gastric Bypass Surgery: A Comprehensive Guide
Guide to Gastric Bypass Surgery
Gastric bypass surgery is considered the "gold standard" when it comes to weight loss surgery. Over 200,000 people opt for weight loss surgery every year, and gastric bypass is one of the most frequently performed procedures.
But what exactly does the surgery entail? Who's an ideal candidate? And what does life look like after you've had your gastric bypass?
This guide covers everything you need to know about gastric bypass, from pre-op prep to long-term lifestyle changes.
What is Gastric Bypass Surgery?
Gastric bypass, also known as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB), is a weight loss surgery procedure that involves creating a small pouch from the stomach and connecting it directly to the small intestine. This allows food to bypass most of the stomach as well as the first section of the small intestine, limiting how much can be consumed and absorbed by the body.
There are a few different types of bariatric surgery procedures, including:
-
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) - The small stomach pouch is connected to the mid-section of the small intestine, bypassing the rest of the stomach and the upper section of the small intestine. This is the most common gastric bypass procedure, with a 70-80% success rate for significant long-term weight loss.

-
Biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD-DS) - A more radical version of gastric bypass that removes 80% of the stomach. This procedure demonstrates the highest rates of weight loss but has more nutritional deficiencies and complications.
-
Vertical sleeve gastrectomy (VSG) - The surgeon removes 85% of the stomach, leaving only a narrow tube-shaped stomach. VSG has fewer complications and nutritional deficiencies than gastric bypass. Success rates are slightly lower than RYGB, with patients losing 60-70% of excess body weight.
-
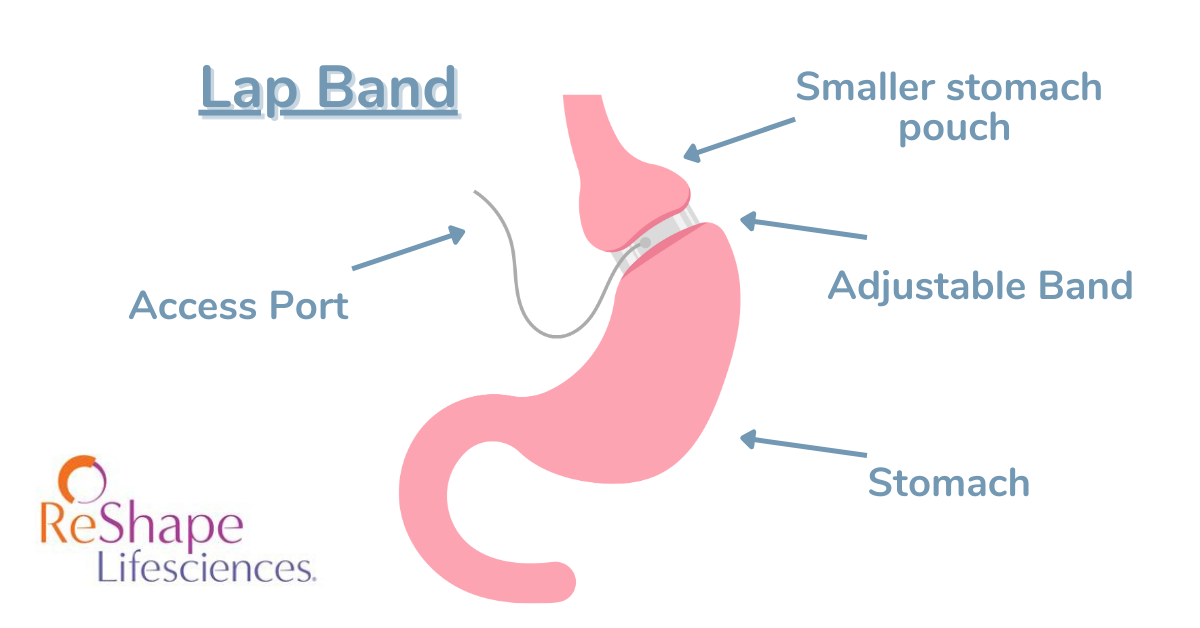
Adjustable gastric band - An inflatable band placed around the upper portion of the stomach. This is the least invasive option, but weight loss results tend to be lower than other procedures. Only 48% of excess weight lost, on average.
| Type of Surgery | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Gastric Bypass | Greatest % of excess weight lost (70-80% long-term). Remission of diabetes. | Nutritional deficiencies likely. Higher complication rate. |
| Biliopancreatic Diversion | Greatest weight loss of all surgeries. | Highest complication and deficiency rates. Not reversible. |
| Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy | Fewer deficiencies than bypass. Remission of diabetes. | Slightly less weight loss than gastric bypass. Not reversible. |
| Adjustable Gastric Band | Least invasive procedure. Fewest deficiencies. Reversible. | More follow-up appointments. Lower % of weight lost. |
Now that we've compared the types of procedures, let's dive deeper into gastric bypass specifically.
Who is a Candidate for Gastric Bypass?
Gastric bypass surgery is for those considered morbidly obese, meaning they have:
- A BMI of 40 or higher
- A BMI of 35 or higher with other comorbid conditions made worse by obesity, like heart disease or diabetes
Typically, candidates for bariatric surgery are unable to lose significant weight through diet and exercise alone. Obese individuals struggle against biology - research shows hormones that drive hunger and fat storage often prevent meaningful change.
“I tried every diet under the sun but just could not keep weight off. Gastric bypass gave me control over my hunger hormones so I could finally make healthy diet and lifestyle choices.” - Sarah D., gastric bypass patient
Psychological screening is a key part of determining if one is ready for the procedure. Those with untreated eating disorders, clinical depression or other uncontrolled mental illnesses may not be immediate candidates. These conditions can sabotage success after surgery if not properly addressed.
Overall, those who have struggled with obesity for years, found little relief from dieting, and demonstrate emotional readiness can be excellent candidates if they meet the BMI thresholds. Significant lifestyle changes are required both pre and post-op, which we’ll explore next.
Preparing for Gastric Bypass Surgery
Patients who wish to undergo gastric bypass must make several changes to diet, exercise and lifestyle habits prior to surgery. This “pre-hab” helps set the stage for optimal success.
Here are the typical pre-op requirements:
- Switch to a nutritious high-protein, low-carb diet - Weeks or months before surgery, patients are asked to alter their typical eating patterns. Eliminating carbs, sugars and increasing vegetable protein intake helps shrink liver size and improves outcomes.
- Increase cardio and strength training - Building cardiovascular endurance and greater mobility before surgery facilitates recovery. Low impact exercises like swimming or walking are encouraged.
- Quit smoking and limit alcohol - Smoking severely impairs healing and risks major complications. Patients must quit smoking for at least 8 weeks prior to gastric bypass. Alcohol is also restricted before and after surgery.
- Undergo psychological evaluation - Assessing one’s readiness and eliminating untreated mental health barriers is crucial before surgery. This may involve counseling, group therapy, or other interventions.
- Select your surgical team - Researching different surgeons and hospitals for the procedure is highly recommended. An experienced bariatric surgery team greatly influences results.
With the surgeon’s clearance and above preparation completed, you’re ready for the procedure!

The Gastric Bypass Procedure Explained
Here is a step-by-step overview of what happens during RYGB surgery:
-
General anesthesia is administered - Gastric bypass surgery typically takes 2-4 hours and is done laparoscopically with small incisions using a camera for guidance. Patients are fully unconscious under general anesthesia during this time.
-
The stomach is stapled - The surgeon will staple and divide the stomach, leaving only a small pouch able to hold 1-2 ounces of food. This pouch is then attached to the small intestine.
-
The small intestine is rerouted - The upper part of the small intestine (jejunum) is attached to the newly created stomach pouch. Food now bypasses the lower stomach and upper small intestine.
-
The other end of the small intestine is reconnected - The lower end of the small intestine is reattached further down so that digestive juices can mix with the food once its passed through the upper small intestine.
-
The abdominal incisions are closed - After testing for leaks, the laparoscopic incisions are cleanly closed with sutures or surgical glue.
Patients typically stay 1-3 nights in the hospital after surgery where their pain is managed and diet is slowly advanced. Most return to normal activities within 2-4 weeks, though exercise restrictions remain for up to 6 weeks.
“I was nervous about the surgery itself but it went very smoothly. I had some pain and nausea the first week but felt back to normal fairly quickly.” - David G., gastric bypass patient
So what potential complications can crop up?
Initial Side Effects and Complications
As with any major surgery, risks are involved with gastric bypass procedures. However, when performed by an experienced bariatric surgery team, complications are generally rare.
Common initial side effects include:
- Pain and soreness around incision sites
- Nausea, vomiting, dehydration from diet progression
- Fatigue and weakness as the body recovers
These symptoms are normal and resolve within a few weeks as patients heal and adjust.
However, some more serious complications can occasionally occur:
- Anastomotic leaks (when stomach/intestine connections leak) - 2.2% risk
- Blood clots - 2.4% risk
- Wound infections - 1.8% risk
- Bowel obstructions - 3.1% risk
Mortality risk from gastric bypass is very low, around 0.3%. The risk of major complications is approximately 4.6%. Your surgical team will monitor you closely for signs of leaks, clots or infection in the initial weeks after surgery while these risks are highest.
| Type of Surgery | Risk of Death | Risk of Complications |
|---|---|---|
| Gastric Bypass | 0.3% | 4.6% |
| Sleeve Gastrectomy | 0.1% | 3.6% |
| Band Surgery | 0.1% | 4.0% |
| Biliopancreatic Diversion | 1.1% | 10.0% |
With the hardest part over - the surgery itself - let’s explore life in the months and years following gastric bypass when the real transformation begins!

Diet and Lifestyle After Gastric Bypass
After surgery, the stomach can only hold a tiny amount of food. Patients must follow a progression from clear liquids to purees, to soft proteins, eventually reintroducing regular textures over several months. Nutritional guidelines after gastric bypass are vital for health.

Here is a sample diet progression:
Stage 1 (Weeks 1-2) - Clear liquids only (broths, gelatins, water, unsweetened teas)
Stage 2 (Weeks 3-4) - High protein smoothies, unsweetened yogurt, sugar-free pudding
Stage 3 (Weeks 5-6) - Pureed soups, mashed fruits/veggies, refried beans, protein shakes
Stage 4 (Months 2-3) - Soft cooked eggs, fish, beans, well-cooked vegetables, shredded chicken
Stage 5 (Months 4-6) - Reintroduce regular textures in small portion sizes
Consuming 60-100 grams of protein daily, drinking 64 oz of fluid, and taking vitamins are also vital for the rapid weight loss and healing that follows surgery. Patients who fail to follow post-op guidelines risk serious deficiencies, malnutrition, and poor outcomes.
"My bariatric team gave me clear instructions on what to eat after surgery. It was challenging at first but I could quickly see following the diet was allowing my body to heal properly as I shed weight." - Julie R., gastric bypass patient
Long-term Outlook After Surgery
So once you’ve recovered from surgery and transitioned into regular foods again - what changes can be expected long-term?
For gastric bypass patients, the 12-24 months after surgery are where the most rapid change occurs. On average:
- Patients lose 70-80% of their excess body weight in the 2 years following surgery
- Over 95% of patients with type 2 diabetes see complete remission after surgery
- Major improvements also seen in other obesity-linked diseases:
- 76% remission rate for hypertension
- 86% remission rate for sleep apnea
- 75% improvement in hyperlipidemia
- 65% improvement in osteoarthritis
In addition to physical health changes, the impact bariatric surgery can have on emotional health and body image is profound. In one study, over 96% of patients reported an improved quality of life after their procedure.
However, continuing to follow diet and exercise guidelines is imperative for long-term success decades after surgery. Some patients experience weight re-gain 10+ years later without appropriate lifestyle management.
“I’ve kept my weight off over 15 years after gastric bypass. It’s given me my life back, but I still have to eat healthy and exercise regularly to stay successful." - Brian L., bariatric surgery patient
Finding Support As a Bariatric Patient
Embarking on the road of weight loss surgery and recovery can feel lonely without adequate support. That’s why we highly recommend new patients join our free online forums or in-person support groups.
Connecting with those who’ve gone through the same journey is invaluable. Our bariatric patients provide inspiration as you tackle challenges post-op and remind you that you’re never alone on this path, no matter what stage you’re in!
We’re thrilled you discovered our guide to gastric bypass surgery. Remember that significant preparation is required before surgery, and diligent adherence to post-op guidelines ensures the best odds of losing excess weight and transforming your health permanently.
Author: Allison Allison, a certified nutritionist and research author, brings over 15 years of experience in the health and weight loss industry. Allison's influence extends through her authorship of multiple health and wellness journals, where she shares her expertise and research on medical weight loss and bariatric medicine. |
Reviewed & Edited By: Dr. K. Huffman Dr. Kevin D. Huffman, D.O., is a board-certified bariatric physician renowned for his expertise in treating obesity. With over 10,000 patients and a reputation as a national leader in bariatric medicine, he has trained hundreds of healthcare providers. As the founder of American Bariatric Consultants, Dr. Huffman develops protocols and training materials sought after by medical societies, pharmaceutical companies, patients, and hospitals. |
Bariatric Guides & Information
More Info
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.